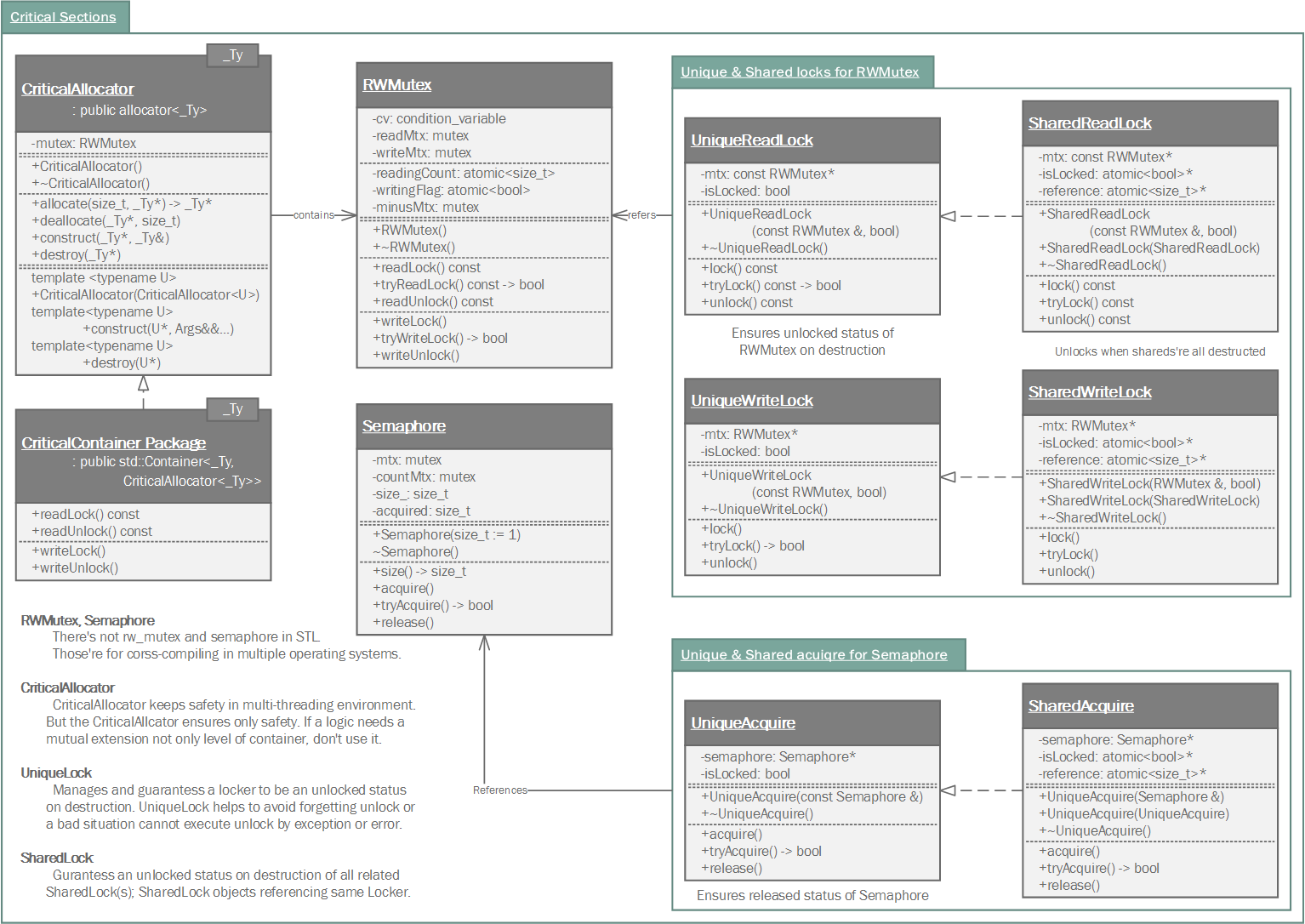
|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
A semaphore. More...
#include <Semaphore.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| Semaphore (size_t=2) | |
| void | setSize (size_t) |
| Set size. More... | |
| auto | size () const -> size_t |
| Get size. More... | |
| auto | acquiredSize () const -> size_t |
| Get acquired size. More... | |
| void | acquire () |
| Acquire admission. More... | |
| auto | tryAcquire () -> bool |
| Try to acquire admission. More... | |
| void | release () |
| Release an admission. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| size_t | size_ |
| The size. More... | |
| size_t | acquired |
| Acquired count. More... | |
| std::mutex * | mtx |
| Locker. More... | |
A semaphore.
In computer science, particularly in operating systems, a semaphore is a variable or abstract data type that is used for controlling access, by multiple processes, to a common resource in a concurrent system such as a multiprogramming operating system.
A trivial semaphore is a plain variable that is changed (for example, incremented or decremented, or toggled) depending on programmer-defined conditions. The variable is then used as a condition to control access to some system resource.
A useful way to think of a semaphore as used in the real-world systems is as a record of how many units of a particular resource are available, coupled with operations to safely (i.e., without race conditions) adjust that record as units are required or become free, and, if necessary, wait until a unit of the resource becomes available. Semaphores are a useful tool in the prevention of race conditions; however, their use is by no means a guarantee that a program is free from these problems. Semaphores which allow an arbitrary resource count are called counting semaphores, while semaphores which are restricted to the values 0 and 1 (or locked/unlocked, unavailable/available) are called binary semaphores
Referenced Wediapedia
Of course, semaphore is already defined in linux C and MFC in Window. But it is dependent on each operating system, so that cannot be compiled in another OS with those semaphores. There's not a class like semaphore in STL yet. It's the reason why Semaphore is provided.
As that reason, if STL supports the semaphore in near future, the Semaphore can be deprecated.
Definition at line 51 of file Semaphore.hpp.
| Semaphore::Semaphore | ( | size_t | size = 2 | ) |
Constructor.
| size | The size of the semaphore to permit |
Definition at line 12 of file Semaphore.cpp.
| void Semaphore::setSize | ( | size_t | val | ) |
| auto Semaphore::size | ( | ) | const -> size_t |
Get size.
Returns size which means the permitted count of the semaphore
Definition at line 36 of file Semaphore.cpp.
| auto Semaphore::acquiredSize | ( | ) | const -> size_t |
Get acquired size.
Definition at line 40 of file Semaphore.cpp.
| void Semaphore::acquire | ( | ) |
Acquire admission.
Acquires an admission and increases count of admission by 1.
If the count is over permitted size, wait until other admissions to be released.
Definition at line 50 of file Semaphore.cpp.
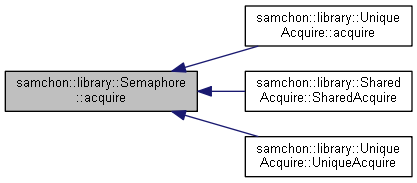
Referenced by samchon::library::UniqueAcquire::acquire(), samchon::library::SharedAcquire::SharedAcquire(), and samchon::library::UniqueAcquire::UniqueAcquire().
| auto Semaphore::tryAcquire | ( | ) | -> bool |
Try to acquire admission.
If admission count is below the permitted size, acquire admission and increase the count by 1 and return true which means succeded to get admission.
Else, do not acquire admission and return false which means failed to get admmission.
Definition at line 60 of file Semaphore.cpp.
| void Semaphore::release | ( | ) |
Release an admission.
Releases an admission what you've acquired. If the admission count was over the limited size, unlock the mutex.
Definition at line 75 of file Semaphore.cpp.
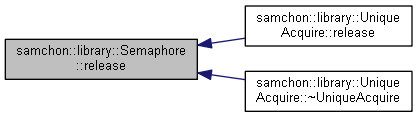
Referenced by samchon::library::UniqueAcquire::release(), and samchon::library::UniqueAcquire::~UniqueAcquire().
|
private |
|
private |
Acquired count.
Definition at line 66 of file Semaphore.hpp.
|
private |