|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
A genetic algorithm class. More...
#include <GeneticAlgorithm.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| GeneticAlgorithm (bool unique, double mutationRate=0.015, size_t tournament=10) | |
| Construct from parameters of Genetic Algorithm. More... | |
| auto | evolveGeneArray (std::shared_ptr< GeneArray > individual, size_t population, size_t generation) const -> std::shared_ptr< GeneArray > |
| Evolve a GeneArray. More... | |
| auto | evolvePopulation (std::shared_ptr< Population > population) const -> std::shared_ptr< Population > |
| Evolve population, a mass of GeneArray(es) More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | mutate (std::shared_ptr< GeneArray > individual) const |
| Cause a mutation on the GeneArray. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| bool | unique |
| Whether each element (Gene) is unique in their GeneArray. More... | |
| double | mutationRate |
| Rate of mutate ocurrence. More... | |
| size_t | tournament |
| Size of tournament in selection. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| auto | selection (std::shared_ptr< Population > population) const -> std::shared_ptr< GeneArray > |
| Select the best GeneArray in population from tournament. More... | |
| auto | crossover (std::shared_ptr< GeneArray > &parent1, std::shared_ptr< GeneArray > &parent2) const -> std::shared_ptr< GeneArray > |
| Create a new GeneArray by crossing over two GeneArray(s) More... | |
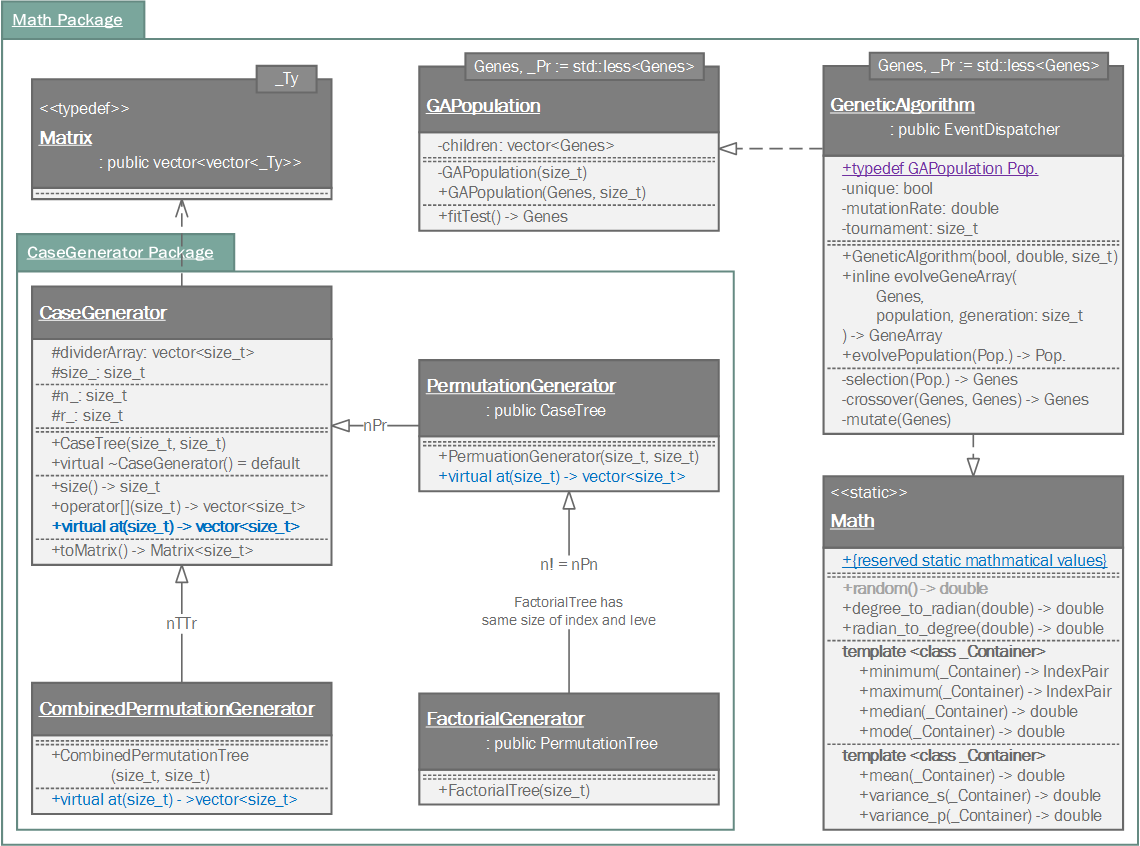
A genetic algorithm class.
In the field of artificial intelligence, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural selection. This heuristic (also sometimes called a metaheuristic) is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems.
Genetic algorithms belong to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA), which generate solutions to optimization problems using techniques inspired by natural evolution, such as inheritance, mutation, selection, and crossover.
Be careful for the mistakes of direction or position of Compare.
Most of logical errors failed to access optimal solution are occured by those mistakens.
| GeneArray | An array(std::vector) containing genes as elments; sequnce listing. The GeneArray must be a type of std::vector. |
| Compare |
A comparison class (or struct) returns whether left gene is more optimal.
Default template parameter of Compare is std::less<GeneArray>. It means to compare two std::vector (GeneArray must be a std::vector). Thus, you've to keep follwing rules.
If you don't want to follow the rules or want a custom comparison class, you have to realize a comparison class. The following code is an example realizing the comparison class.
- GeneArray is inherited from <i>std::vector</i> - GeneArray has custom <i>auto operator<(const GeneArray &) const -> bool</i>
Definition at line 60 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
|
inline |
Construct from parameters of Genetic Algorithm.
| unique | Whether each Gene is unique in their GeneArray |
| mutationRate | Rate of mutation |
| tournament | Size of tournament in selection |
Definition at line 97 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
References samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::mutationRate, samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::tournament, and samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::unique.
|
inline |
Evolve a GeneArray.
Convenient method accessing to evolvePopulation().
| individual | An initial set of genes; sequence listing |
| population | Size of population in a generation |
| generation | Size of generation in evolution |
Definition at line 114 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
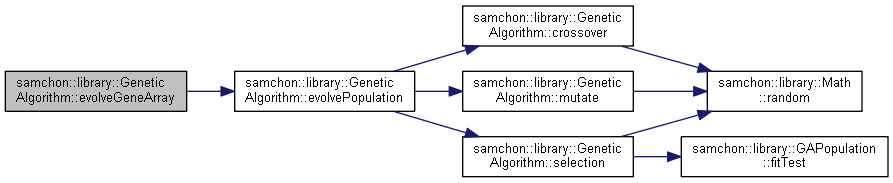
References samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::evolvePopulation().
Referenced by samchon::examples::tsp::Scheduler::optimize().
|
inline |
Evolve population, a mass of GeneArray(es)
| population | An initial population |
Definition at line 129 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
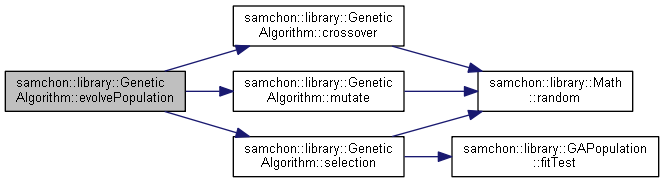
References samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::crossover(), samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::mutate(), and samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::selection().
Referenced by samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::evolveGeneArray().

|
inlineprivate |
Select the best GeneArray in population from tournament.
Selection is the stage of a genetic algorithm in which individual genomes are chosen from a population for later breeding (using crossover operator). A generic selection procedure may be implemented as follows:
| population | The target of tournament |
Definition at line 187 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
References samchon::library::GAPopulation< GeneArray, Compare >::children, samchon::library::GAPopulation< GeneArray, Compare >::fitTest(), and samchon::library::Math::random().
Referenced by samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::evolvePopulation().

|
inlineprivate |
Create a new GeneArray by crossing over two GeneArray(s)
crossover is a genetic operator used to vary the programming of a chromosome or chromosomes from one generation to the next. It is analogous to reproduction and biological crossover, upon which genetic algorithms are based.
Cross over is a process of taking more than one parent solutions and producing a child solution from them. There are methods for selection of the chromosomes.
| parent1 | A parent sequence listing |
| parent2 | A parent sequence listing |
Definition at line 219 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
References samchon::library::Math::random().
Referenced by samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::evolvePopulation().

|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
Cause a mutation on the GeneArray.
Mutation is a genetic operator used to maintain genetic diversity from one generation of a population of genetic algorithm chromosomes to the next. It is analogous to biological mutation.
Mutation alters one or more gene values in a chromosome from its initial state. In mutation, the solution may change entirely from the previous solution. Hence GA can come to better solution by using mutation.
Mutation occurs during evolution according to a user-definable mutation probability. This probability should be set low. If it is set too high, the search will turn into a primitive random search.
Muttion is pursuing diversity. Mutation is useful for avoiding the following problem.
When initial set of genes(GeneArray) is far away from optimail, without mutation (only with selection and crossover), the genetic algorithm has a tend to wandering outside of the optimal.
Genes in the GeneArray will be swapped following percentage of the mutationRate.
| individual | A container of genes to mutate |
Definition at line 294 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
References samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::mutationRate, and samchon::library::Math::random().
Referenced by samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::evolvePopulation().

|
protected |
Whether each element (Gene) is unique in their GeneArray.
Definition at line 69 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
Referenced by samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::GeneticAlgorithm().
|
protected |
Rate of mutate ocurrence.
The mutationRate determines the percentage of occurence of mutation in a GeneArray.
Definition at line 82 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
Referenced by samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::GeneticAlgorithm(), and samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::mutate().
|
protected |
Size of tournament in selection.
Definition at line 87 of file GeneticAlgorithm.hpp.
Referenced by samchon::library::GeneticAlgorithm< GeneArray, Compare >::GeneticAlgorithm().