|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
An Entity and a static array containing Entity objects. More...
#include <EntityArray.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| EntityArray () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| virtual void | construct (std::shared_ptr< library::XML > xml) override |
| Construct data of the Entity from an XML object. More... | |
| virtual auto | toXML () const -> std::shared_ptr< library::XML > override |
| Get an XML object represents the EntityArray. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::Entity Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::Entity | |
| virtual auto | TAG () const -> std::string=0 |
| A tag name when represented by XML. More... | |
| Entity () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| virtual auto | key () const -> std::string |
| Get a key that can identify the Entity uniquely. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup | |
| IEntityGroup () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup Protected Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup | |
| virtual auto | CHILD_TAG () const -> std::string=0 |
| A tag name of children. More... | |
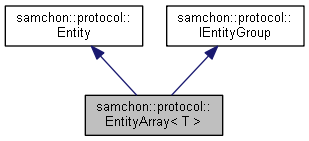
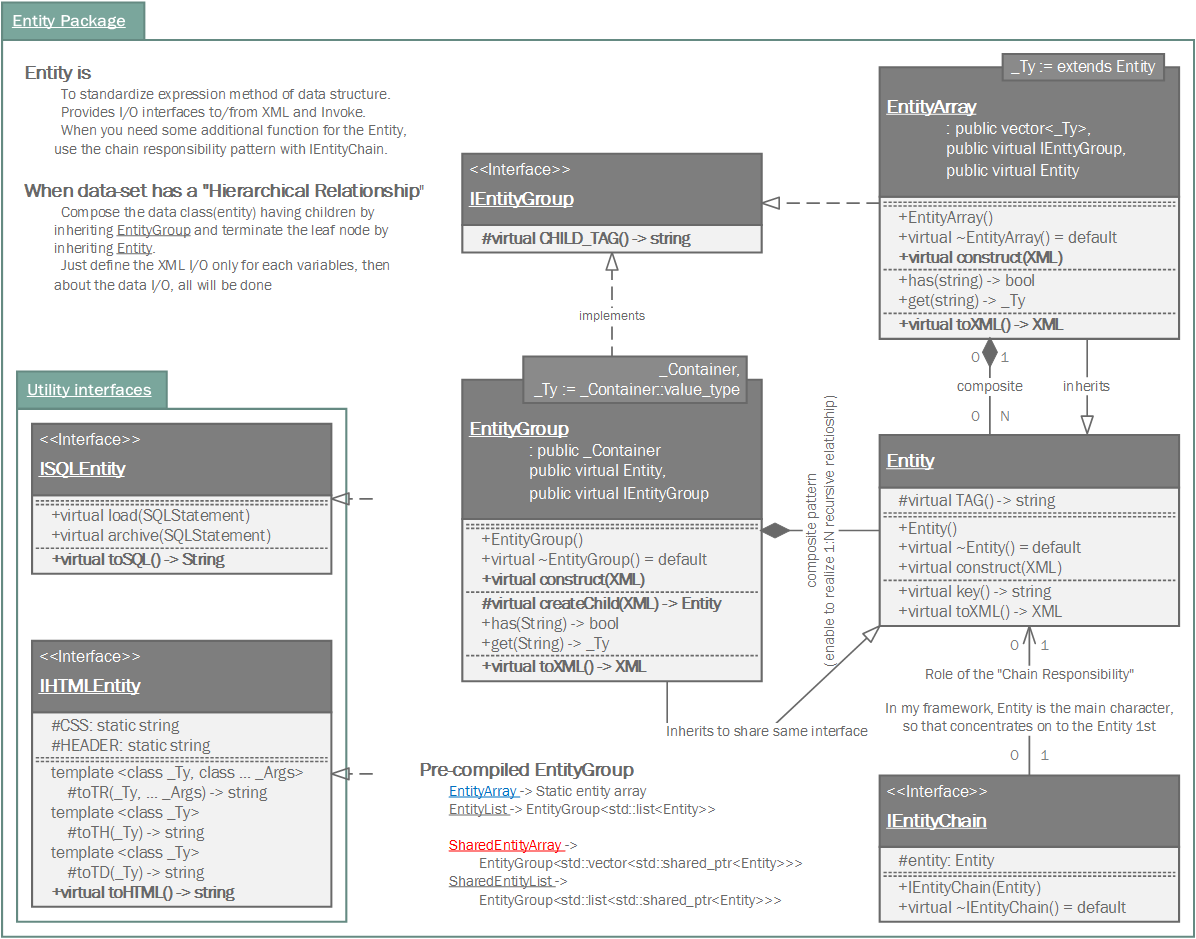
An Entity and a static array containing Entity objects.
EntityArray is a static array containing children objects derived from an Entity class.
The EntityArray has advantages of performance like fast iteration or fast access because the EntityArray is serialized. However, as EntityArray is serialized, allocated memory space for each child is fixed and cannot contain derived a entity class from the child entity type.
Thus, it's suitable for when fast accessment and iteration like an entity class containing mathmatical or statistical data and methods which doesn't seemed to be inherited.
Entity is a class for standardization of expression method using on network I/O by XML. If Invoke is a standard message protocol of Samchon Framework which must be kept, Entity is a recommended semi-protocol of message for expressing a data class. Following the semi-protocol Entity is not imposed but encouraged.
As we could get advantages from standardization of message for network I/O with Invoke, we can get additional advantage from standardizing expression method of data class with Entity. We do not need to know a part of network communication. Thus, with the Entity, we can only concentrate on entity's own logics and relationships between another entities. Entity does not need to how network communications are being done.
I say repeatedly. Expression method of Entity is recommended, but not imposed. It's a semi protocol for network I/O but not a essential protocol must be kept. The expression method of Entity, using on network I/O, is expressed by XML string.
If your own network system has a critical performance issue on communication data class, it would be better to using binary communication (with ByteArray or boost::serialization). Don't worry about the problem! Invoke also provides methods for binary data (ByteArray).
If a data structure has recursive and hierarchical relationship, never use the EntityArray. EntityArray's memory allocation is static. The recursive relationship causes infinite memory allocation. It must generates stack overflow.
Use EntityGroup instead.
Definition at line 47 of file EntityArray.hpp.
|
inline |
Default Constructor.
Definition at line 59 of file EntityArray.hpp.
|
inlineoverridevirtual |
Construct data of the Entity from an XML object.
Constructs the EntityArray's own member variables only from the input XML object.
Do not consider about constructing children Entity objects' data in EntityArray::construct(). Those children Entity objects' data will constructed by their own construct() method. Even insertion of XML objects representing children are done by abstract method of EntityArray::toXML().
Constructs only data of EntityArray's own.
Overrides the construct() method and fetch data of member variables from the XML.
By recommended guidance, data representing member variables are contained in properties of the put XML object.
| xml | An xml used to construct data of entity |
Implements samchon::protocol::Entity.
Definition at line 76 of file EntityArray.hpp.
References samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup::CHILD_TAG().
|
inlineoverridevirtual |
Get an XML object represents the EntityArray.
Archives the EntityArray's own member variables only to the returned XML object.
Do not consider about archiving children Entity objects' data in EntityArray::toXML(). Those children Entity objects will converted to XML object by their own toXML() method. The insertion of XML objects representing children are done by abstract method of EntityArray::toXML().
Archives only data of EntityArray's own.
Returns an XML object that can represents the Entity containing member variables into properties.
A member variable (not object, but atomic value like number, string or date) is categorized as a property within the framework of entity side. Thus, when overriding a toXML() method and archiving member variables to an XML object to return, puts each variable to be a property belongs to only an XML object.
Don't archive the member variable of atomic value to XML::value causing enormouse creation of XML objects to number of member variables. An Entity must be represented by only an XML instance (tag).
| Standard Usage | Non-standard usage abusing value |
|---|---|
| <memberList> <member id='jhnam88' name='Jeongho+Nam' birthdate='1988-03-11' /> <member id='master' name='Administartor' birthdate='2011-07-28' /> </memberList> | <member> <id>jhnam88</id> <name>Jeongho+Nam</name> <birthdate>1988-03-11</birthdate> </member> |
Reimplemented from samchon::protocol::Entity.
Definition at line 104 of file EntityArray.hpp.
References samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup::CHILD_TAG(), and samchon::protocol::Entity::toXML().