|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
Package of network protocol and libraries. More...
Namespaces | |
| master | |
| Package for external system, within the framework of master. | |
| service | |
| Package of cloud service as a server. | |
| slave | |
| Package of external system, within the framework of slave. | |
Classes | |
| class | Entity |
| An entity, a standard data class. More... | |
| class | EntityArray |
| An Entity and a static array containing Entity objects. More... | |
| class | EntityGroup |
| An Entity and a container of children Entity objects. More... | |
| class | EntityList |
| An Entity and a static list containing Entity objects. More... | |
| class | ExternalClient |
| A network driver for an external client. More... | |
| class | ExternalClientArray |
| An array of ExternalClient(s) More... | |
| class | ExternalServer |
| A network driver for an external server. More... | |
| class | ExternalServerArray |
| An array of ExternalServer(s) More... | |
| class | ExternalSystem |
| A network driver for an external system. More... | |
| class | ExternalSystemArray |
| An array of ExternalSystem(s). More... | |
| class | ExternalSystemRole |
| A role belongs to an external system. More... | |
| class | FlashPolicyServer |
| A flash policy server. More... | |
| class | IClient |
| An interface for a client. More... | |
| class | IEntityChain |
| A chain of entity. More... | |
| class | IEntityGroup |
| An iternface for entity group. More... | |
| class | IHTMLEntity |
| An interface supporting conversion to html. More... | |
| class | Invoke |
| Standard message of network I/O. More... | |
| class | InvokeHistory |
| A history of an Invoke message. More... | |
| class | InvokeHistoryArray |
| An array of InvokeHistory. More... | |
| class | InvokeParameter |
| A parameter of an Invoke. More... | |
| class | IProtocol |
| An interface of Invoke message chain. More... | |
| class | IServer |
| An interface of a physical server. More... | |
| class | ISQLEntity |
| An interface supporting DB-I/O. More... | |
| class | IWebClientBase |
| An interface for a web-client. More... | |
| class | IWebServer |
| An interface for a physical server following web-socket. More... | |
| class | ServerConnector |
| A server connector for a physical client. More... | |
| class | SystemRole |
| A role belongs to a system. More... | |
| class | WebServerConnector |
| A web-socket server connector. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| template<typename _Ty = Entity> | |
| using | SharedEntityArray = EntityGroup< std::vector< std::shared_ptr< _Ty >>, _Ty, std::shared_ptr< _Ty > > |
| An EntityGroup with vector container and children capsuled in shared pointers. More... | |
| template<typename _Ty = Entity> | |
| using | SharedEntityList = EntityGroup< std::list< std::shared_ptr< _Ty >>, _Ty, std::shared_ptr< _Ty > > |
| An EntityGroup with list container and children capsuled in shared pointers. More... | |
| template<typename _Ty = Entity> | |
| using | UniqueEntityArray = EntityGroup< std::vector< std::unique_ptr< _Ty >>, _Ty, std::unique_ptr< _Ty > > |
| An EntityGroup with vector container and children capsuled in unique pointers. More... | |
| template<typename _Ty = Entity> | |
| using | UniqueEntityList = EntityGroup< std::list< std::unique_ptr< _Ty >>, _Ty, std::unique_ptr< _Ty > > |
| An EntityGroup with list container and children capsuled in unique pointers. More... | |
Package of network protocol and libraries.
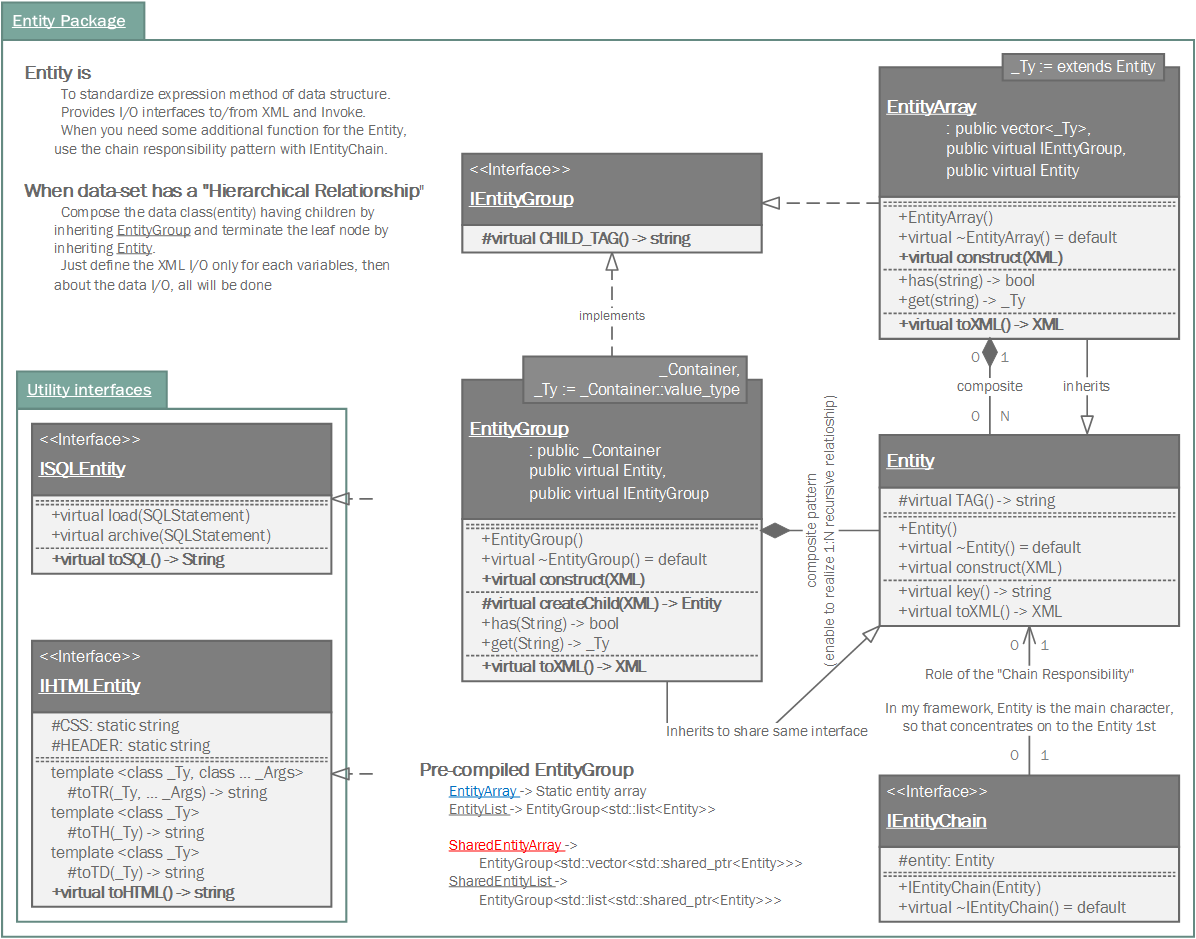
In Samchon Framework, with entity, boundary and control, entity is the main. The entity package provides I/O interface to/from XML, Invoke and DBMS. If you need some additional function (role of boundary or control) for an entity, use chain of responsibility pattern starting from the entity.
When data-set has a "hierarchical relationship", do not have the children objects by having a container member variable. Directly inherits container set. Composes the data class (entity) having children by inheriting EntityGroup and terminate the leaf node by inheriting Entity (single object).
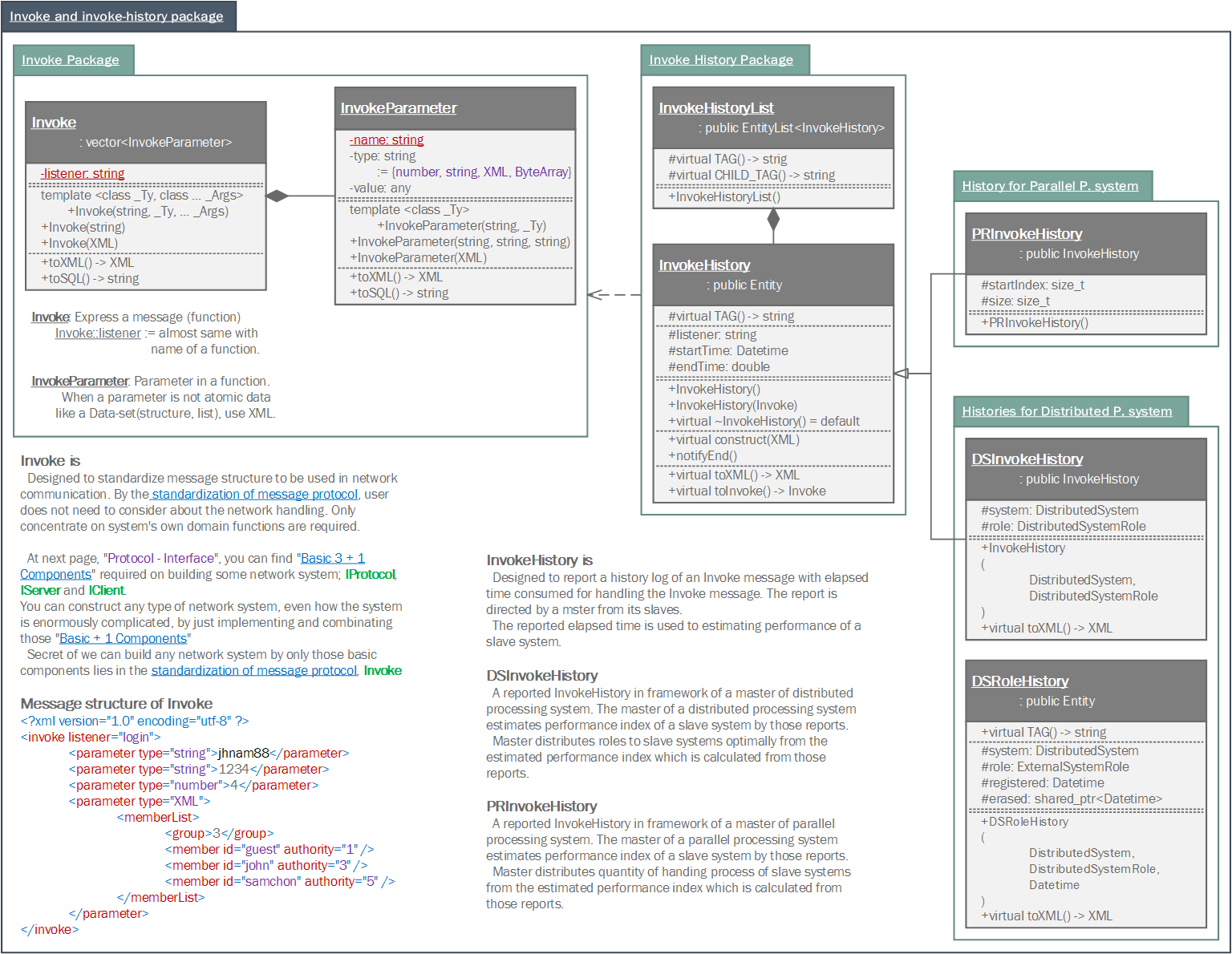
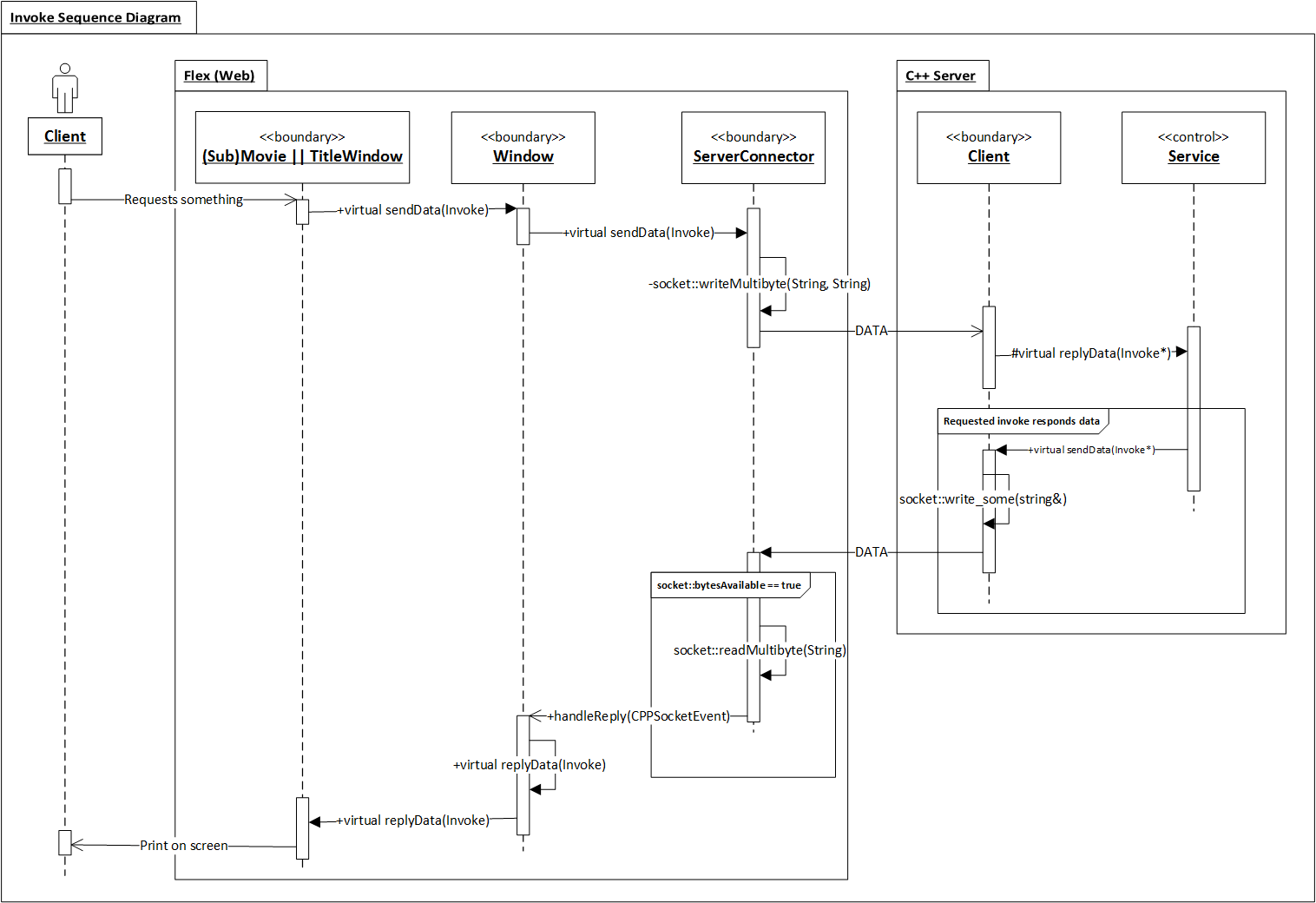
Invoke is a standard message structure using network I/O in Samchon Framework.
The Invoke message has an XML structure like the piacture in below. We can enjoy lots of benefits by the normalized and standardized message structure used in network I/O.
The greatest advantage is that we can make any type of network system, even how the system is enourmously complicated. As network communication message is standardized, we only need to concentrate on logical relationships between network systems. We can handle each network system like a object (class) in OOD. And those relationships can be easily designed by using design pattern.
Furthermore, The module invoke not only provides parsing and converting from/to Invoke message, but also history classes can be used to archiving log or estimating performance of a system. The purpose of estimating performance a system, especially, used in module of distributed processing and parallel processing systems.
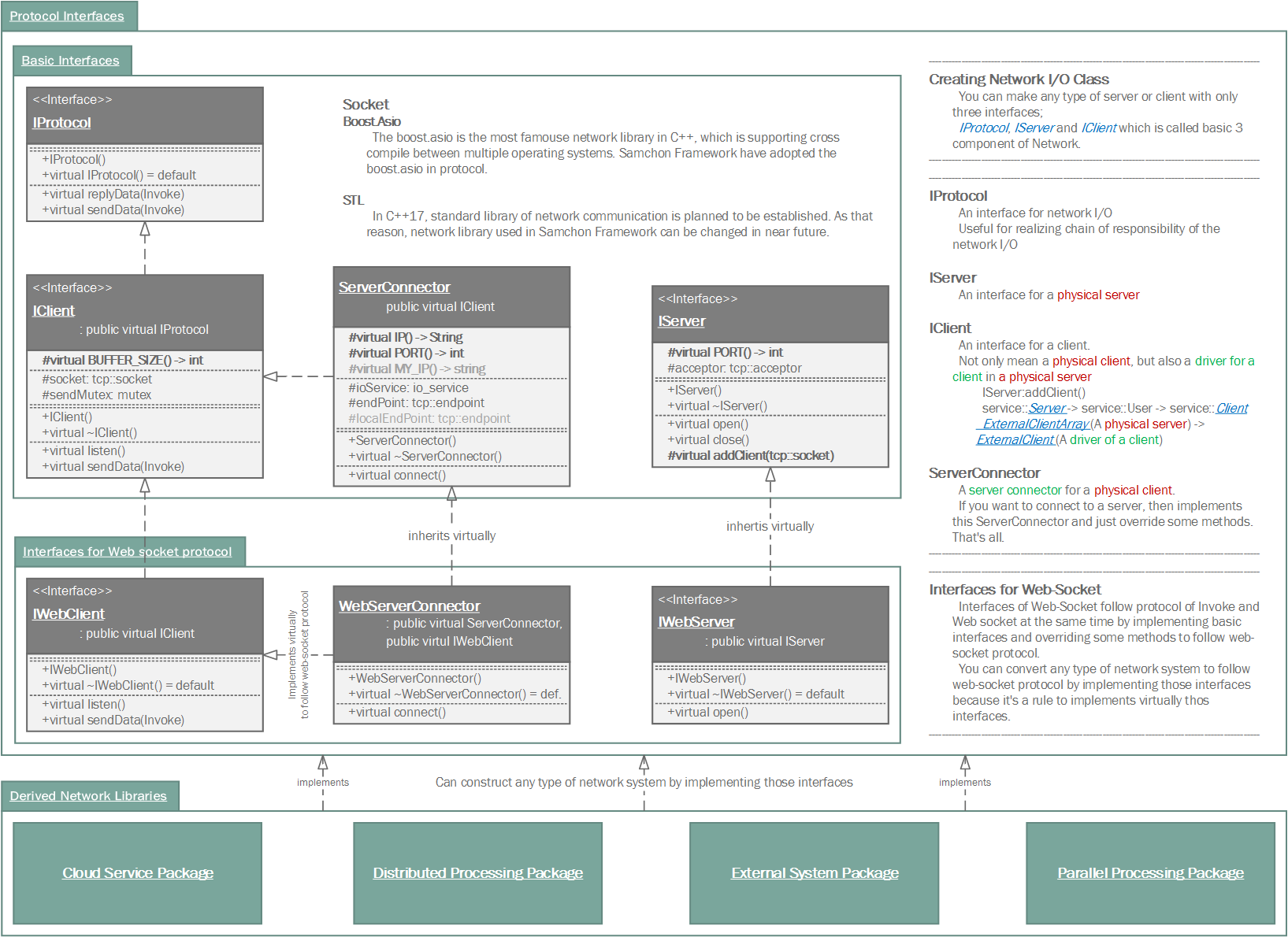
You can make any type of network system with only three + one interfaces; IProtocol, IServer and IClient + ServerConnector which are called basic 3 + 1 components. As I've mentiond in previous invoke module, because of standardization of message of network I/O, we only need to concentrate on logical relationship like handling OOD objects
The basic 3 + 1 components are top level abstract interfaces for designing network system like handling OOD objects. When you see the protocol module from a different view, out of framework, you can find that all the other classes in protocol are another examples combinationing and utilizing those basic 3 + 1 components (interaces).
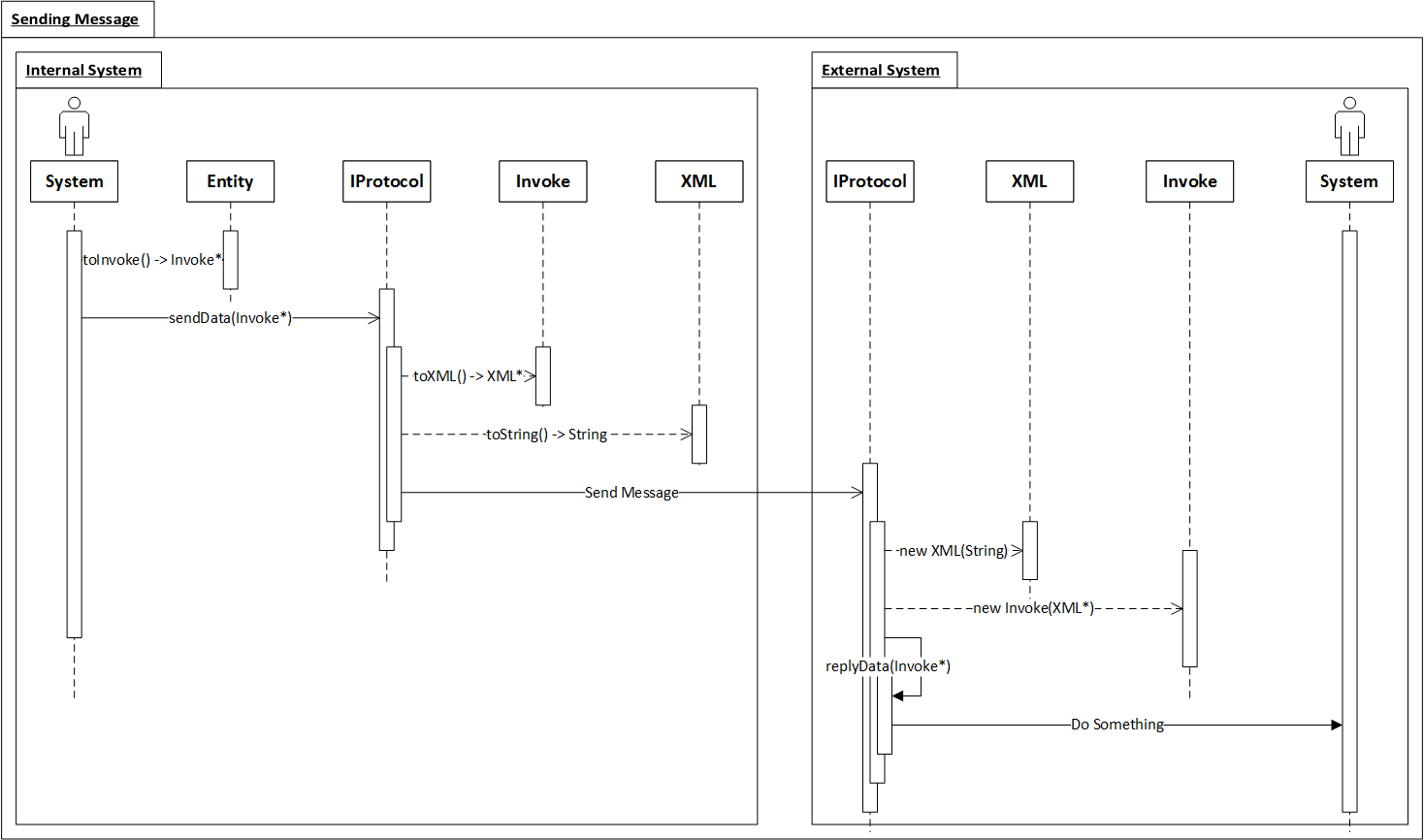
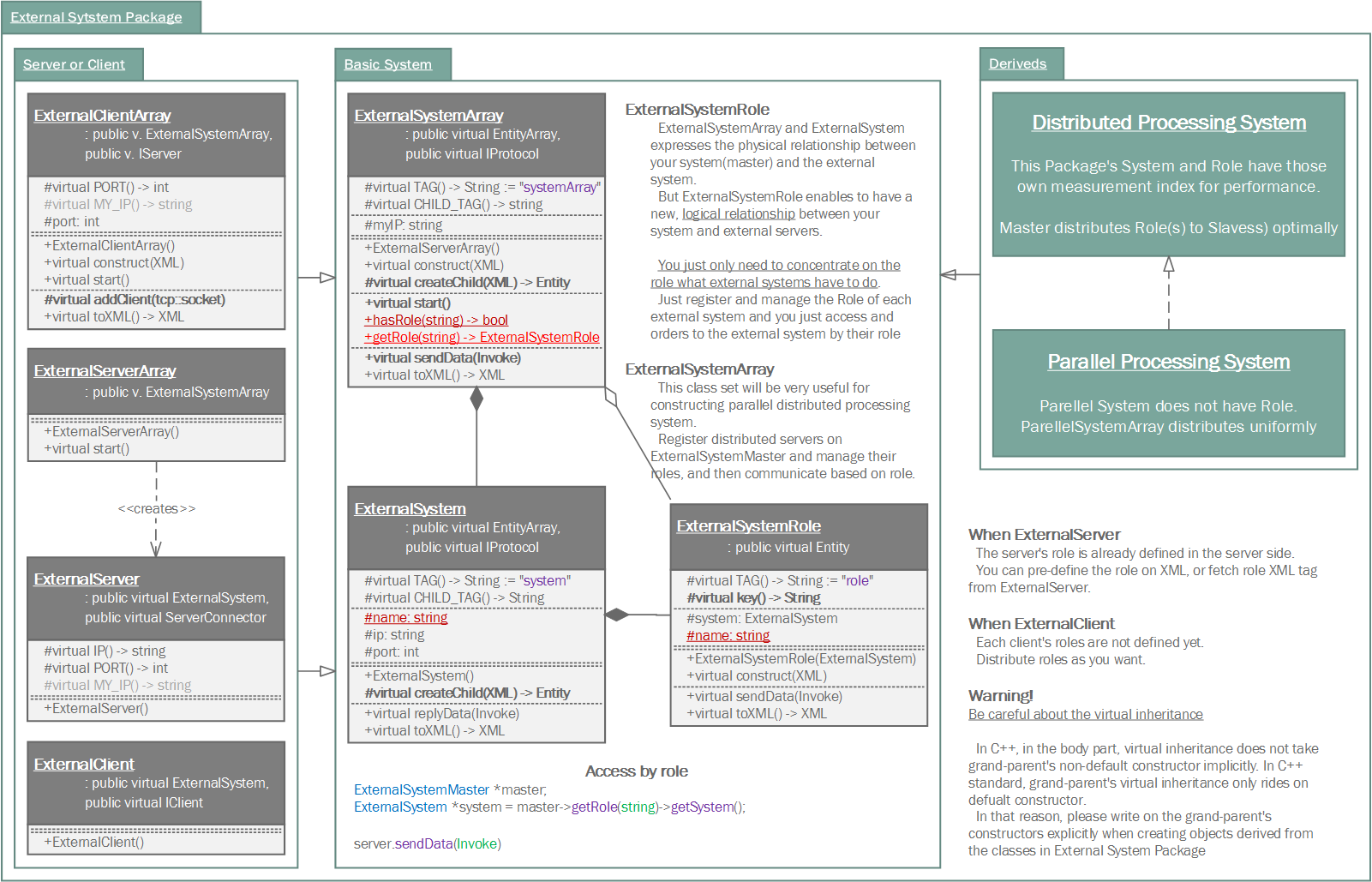
Module external_system provides interfaces for interaction with external network system. Although, the module external_system acts boundary as main role, what you've to concentrate on is the entity. Samchon Framework takes responsibility of network communication and you only consider about relationship and role of each external network systems.
ExternalSystem objects are managed by ExternalSystemArray and the ExternalSystemArray can access to an ExternalSystemRole belongs to an ExternalSystem directly. When you send an Invoke message to ExternalSystemArray, the ExternalSystemArray finds matched ExternalSystemRole and the ExternalSystemRole shifts the network I/O responsibility to belonged ExternalSystem.
The relationship called as "Proxy Pattern". With the pattern, "Proxy", you can concentrate on roles irrespective of where each role is belonged to (you can only concentrate on ExternalSystemRole itself, what to do with Invoke message, irrespective of the ExternalSystemRole is belonged to which ExternalSystem).
Whether using the "Proxy pattern" is on your mind in external_system module level. "Proxy pattern" is recommend to use in external_system module, but not forced. However, since parallel_processing_system module, you've to follow the pattern.
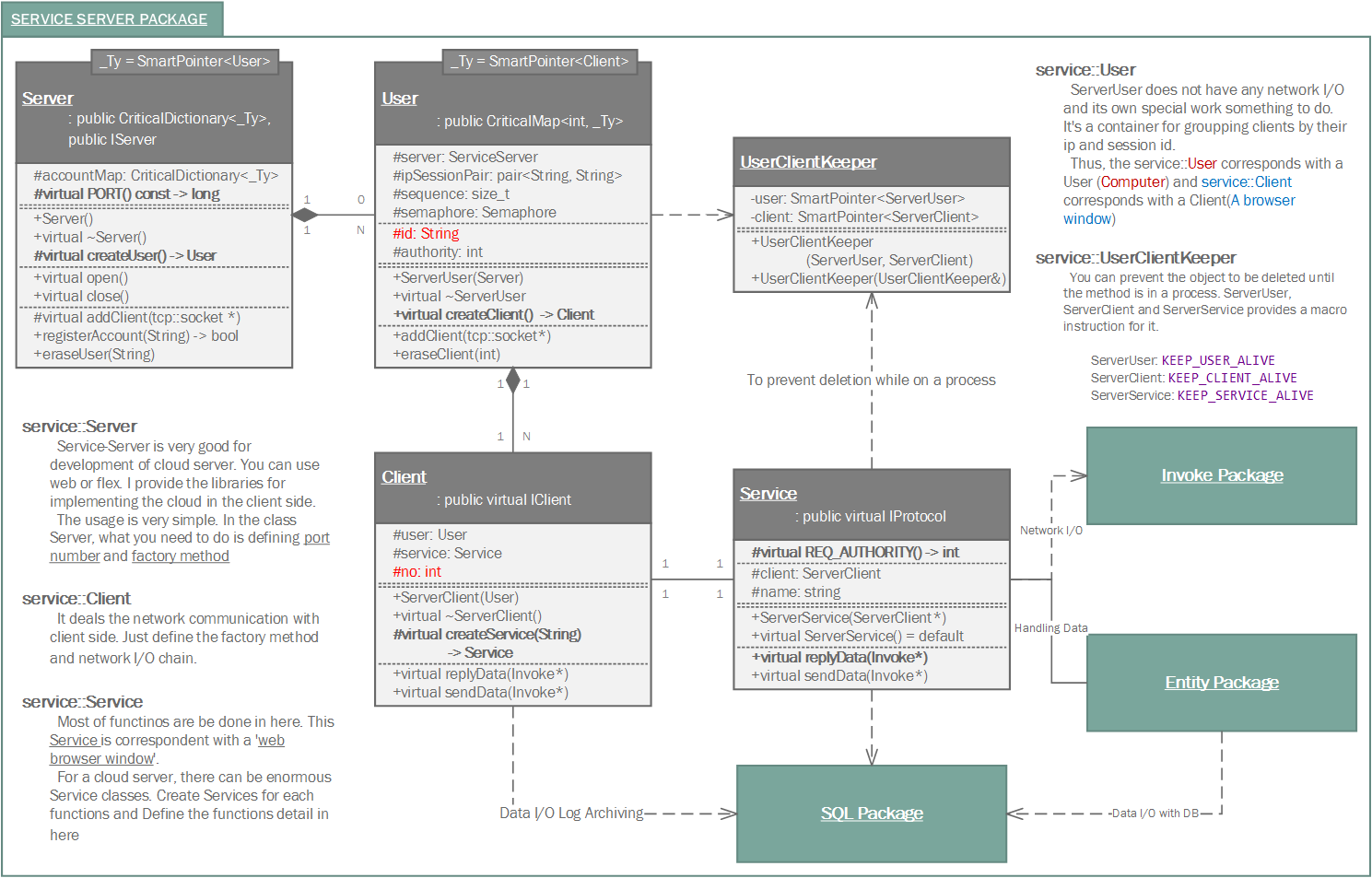
The "service" package is for realizing cloud service.
In Samchon Framework, realizing cloud service, there're two classes representing physical server and client as service::Server and service::Client. Between the two classes representing boundaries, there is a class representing logical conception user as service::User. In the terminal node under the service::Client, service::Service class represents a control.
The default protocol of the service package is not 'web socket'. The default only has message protocol of Invoke, does not have handshake or another pre-defined protocol. By the default protocol, you can connect to the cloud server (built from c++, by service package) as a client by a program or plug-in like Flex or C#. However you can't connect by web-browser only allowing socket protocol as web-socket.
To build a cloud service to follow web-socket protocol, inherits derviced classes not from service::Server, service::Client, but from service::WebServer, service::WebClient or implements IWebServer, IWebClient which are derived from service::Server and service::Client.
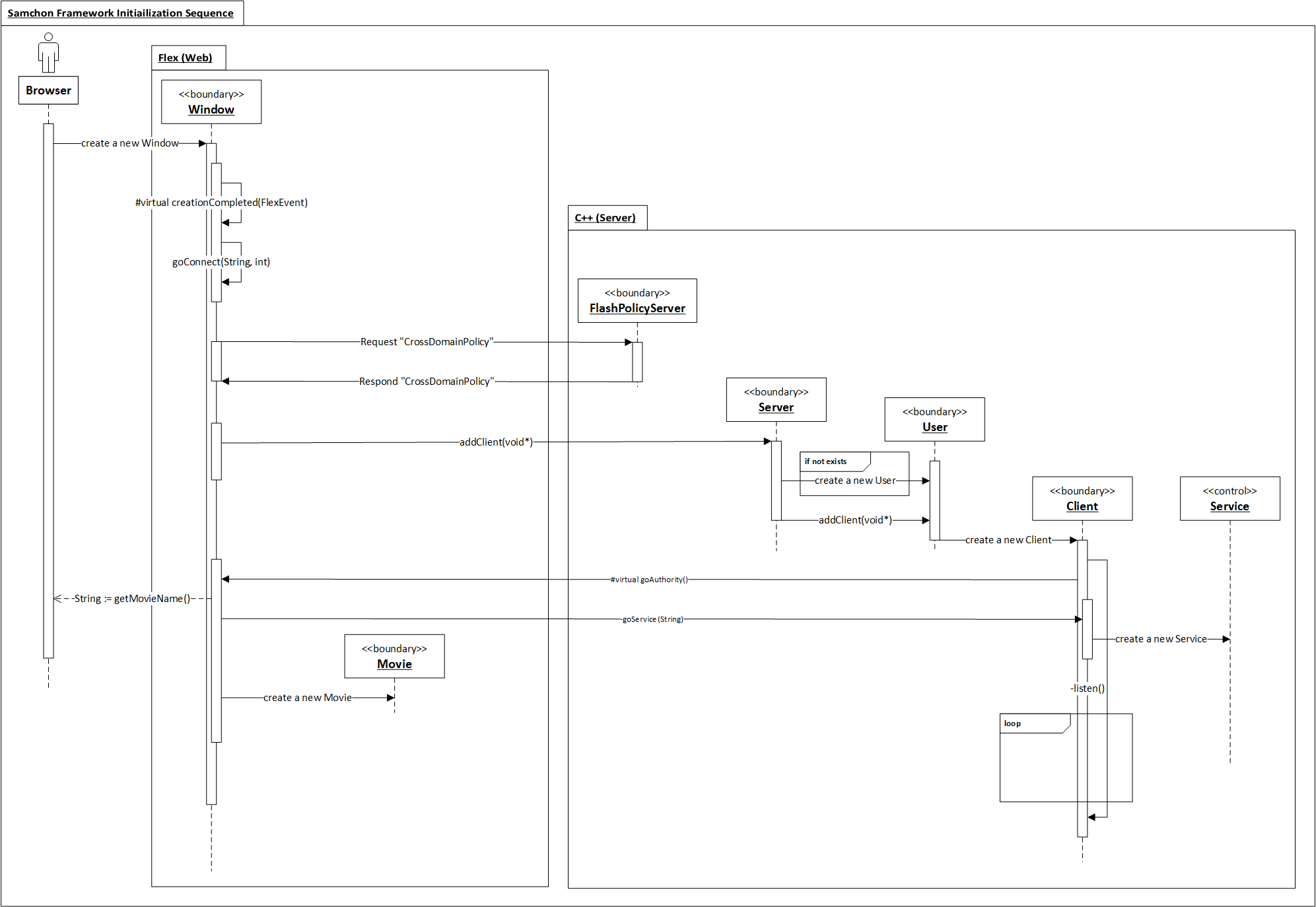
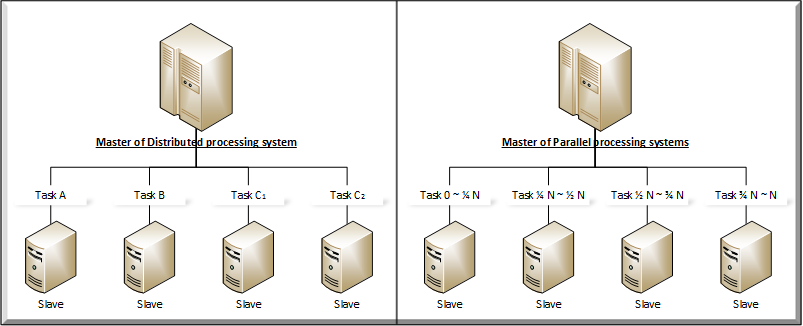
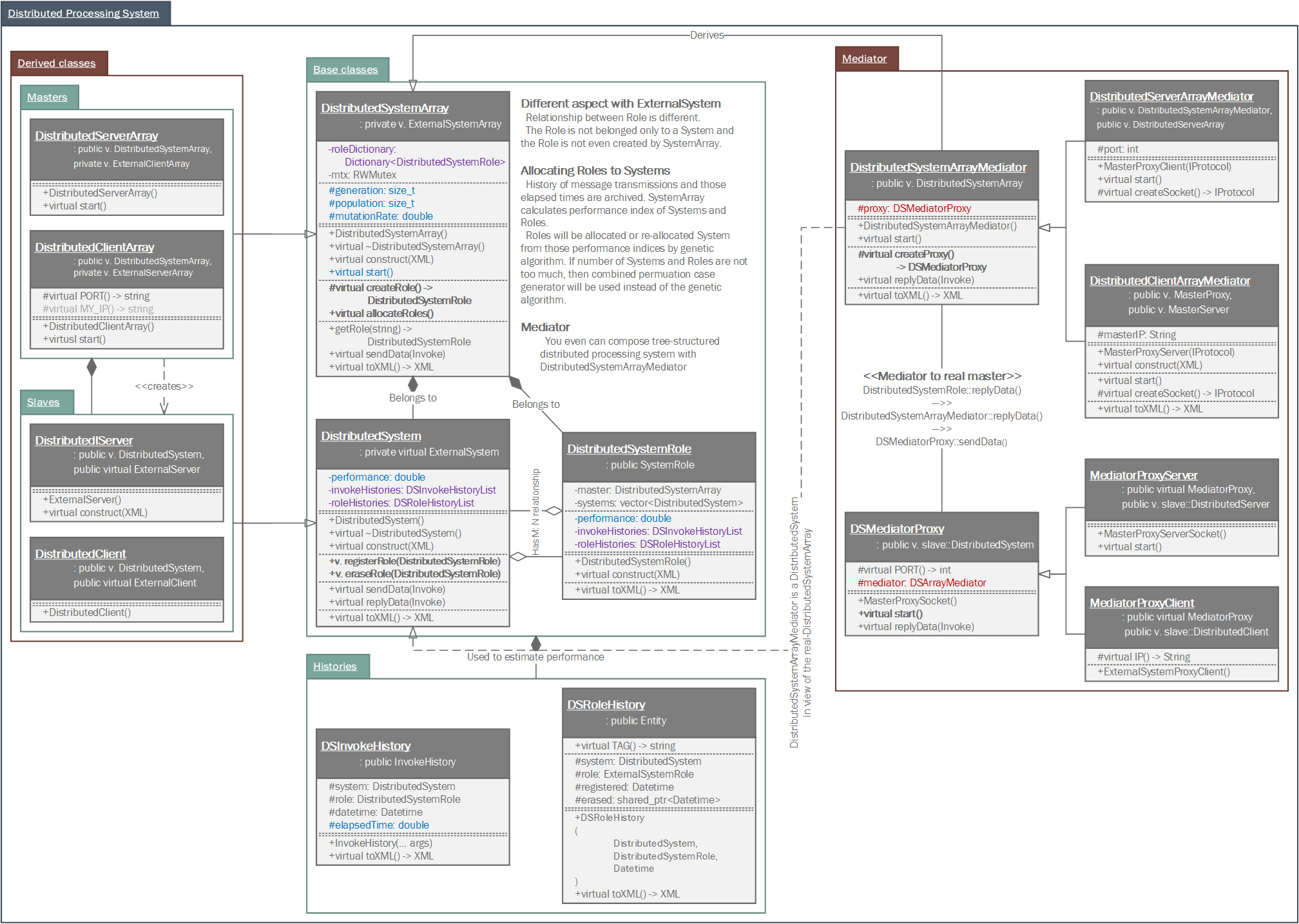
In master package, provides distributed and parallel processing system modules which are in framework of master. With classes in master package, you can realize any type of distributed or parallel processing system in master side, even how enormouse scale those have.
A distributed processing system of master, a master (master::DistributedSystemArray) allocates roles (master::DistributedSystemRole) to systems (master::DistributedSystem). User does not consider about which roles are allocated to which systems. User just accesses to a role and send or reply message from those roles.
It's the proxy pattern have mentioned in external system
ExternalSystem objects are managed by ExternalSystemArray and the ExternalSystemArray can access to a role belongs to a system directly. When you send an Invoke message to ExternalSystemArray, the ExternalSystemArray finds matched ExternalSystemRole and the ExternalSystemRole shifts the network I/O responsibility to belonged ExternalSystem. This relationship called "Proxy Pattern". By the pattern, "Proxy", you can concentrate on roles irrespective of where each role is belonged to.
However, unlike the case of managing roles from ExternalSystemArray, in DistributedSystemArray, roles can be allocated in multiple systems duplicately. And the roles can be moved to another systems. Those management and allocation of roles are determined by estimation of performance of each system, and required performance of each role.
Unlike distributed processing system, the parallel processing system is not complicate. It has very simple logic. About requested processes, master(master::ParallelSystemArray) allocates each process to each slave system by their own performance index have estimated.
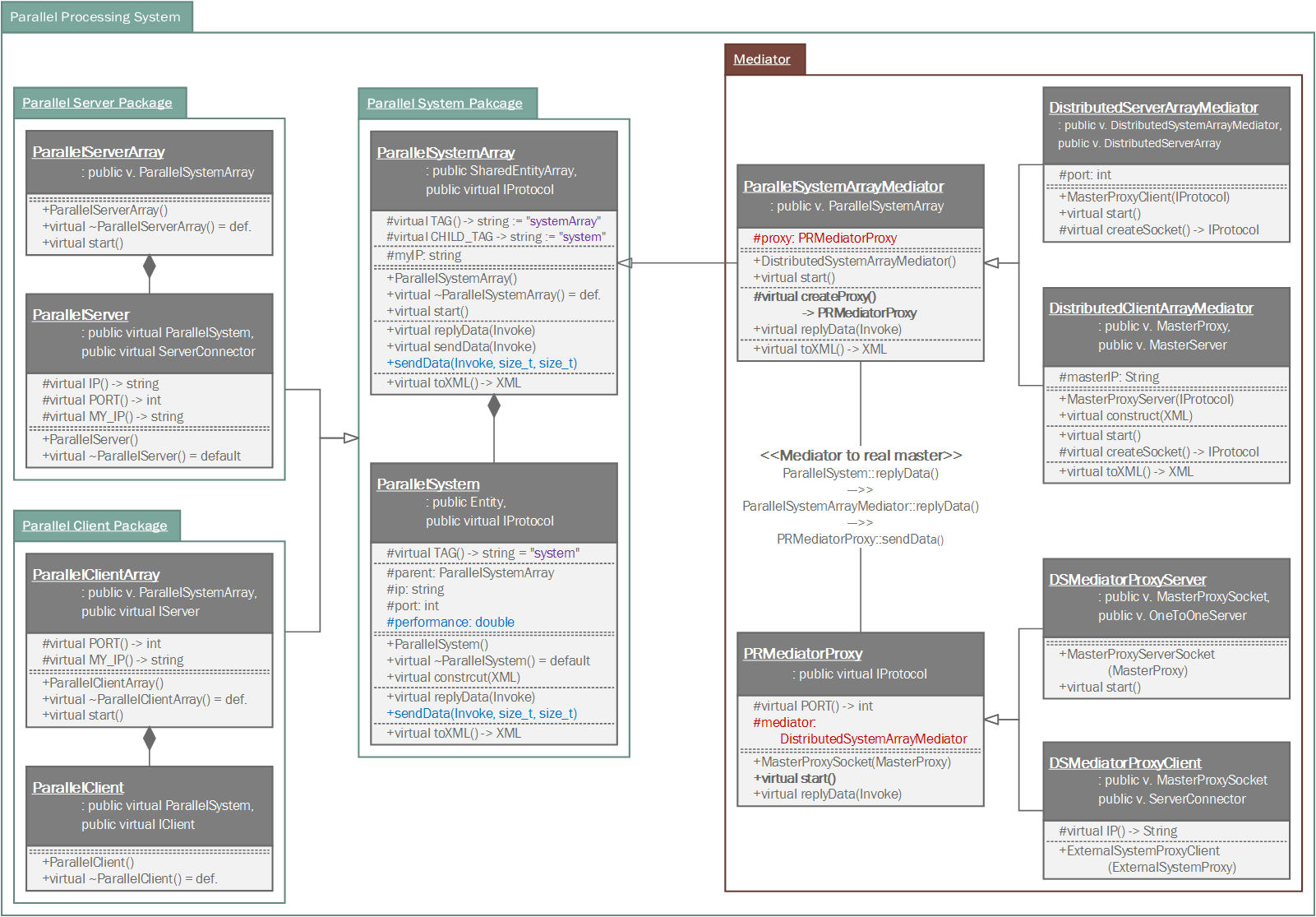
A package for composing distributed or parallel processing system in slave side.
Slave system get orders from master, processes the orders and report the result with its elapsed time for estimating performance of the slave system.

| using samchon::protocol::SharedEntityArray = typedef EntityGroup < std::vector<std::shared_ptr<_Ty>>, _Ty, std::shared_ptr<_Ty> > |
An EntityGroup with vector container and children capsuled in shared pointers.
| _Ty | A type of children Entity. Must be a class derived from an Entity or Entity itself. |
For a case of inheritance of SharedEntityArray and the inherited SharedEntityArray also contains entity objects which are inherited from original child entity type, SharedEntityArray supports macros changing returned type of accessor methods.
Definition at line 32 of file SharedEntityArray.hpp.
| using samchon::protocol::SharedEntityList = typedef EntityGroup < std::list<std::shared_ptr<_Ty>>, _Ty, std::shared_ptr<_Ty> > |
An EntityGroup with list container and children capsuled in shared pointers.
| _Ty | A type of children Entity. Must be a class derived from an Entity or Entity itself. |
Definition at line 24 of file SharedEntityList.hpp.
| using samchon::protocol::UniqueEntityArray = typedef EntityGroup < std::vector<std::unique_ptr<_Ty>>, _Ty, std::unique_ptr<_Ty> > |
An EntityGroup with vector container and children capsuled in unique pointers.
| _Ty | A type of children Entity. Must be a class derived from an Entity or Entity itself. |
For a case of inheritance of UniqueEntityArray and the inherited UniqueEntityArray also contains entity objects which are inherited from original child entity type, UniqueEntityArray supports macros changing returned type of accessor methods.
std::unique_ptr doesn't allow copy construction. It allows only move construction. When inserts children objcets not by construct() method but by your hand, Be careful to insert deriving copy construction. You've use move constructor.
Definition at line 39 of file UniqueEntityArray.hpp.
| using samchon::protocol::UniqueEntityList = typedef EntityGroup < std::list<std::unique_ptr<_Ty>>, _Ty, std::unique_ptr<_Ty> > |
An EntityGroup with list container and children capsuled in unique pointers.
| _Ty | A type of children Entity. Must be a class derived from an Entity or Entity itself. |
std::unique_ptr doesn't allow copy construction. It allows only move construction. When inserts children objcets not by construct() method but by your hand, Be careful to insert deriving copy construction. You've use move constructor.
Definition at line 32 of file UniqueEntityList.hpp.