|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
|
Samchon Framework for CPP
1.0.0
|
A network driver for a distributed system. More...
#include <DistributedSystem.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| DistributedSystem () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| virtual void | construct (std::shared_ptr< library::XML >) override |
| Construct data of the Entity from an XML object. More... | |
| virtual void | sendData (std::shared_ptr< Invoke >) override |
| Sends message to a related system. More... | |
| virtual void | replyData (std::shared_ptr< Invoke >) override |
| Handling replied message from an external system. More... | |
| virtual auto | toXML () const -> std::shared_ptr< library::XML > override |
| Get an XML object represents the EntityGroup. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem | |
| ExternalSystem () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| virtual void | start ()=0 |
| Start interaction. More... | |
| virtual auto | key () const -> std::string override |
| Get a key that can identify the Entity uniquely. More... | |
| virtual auto | TAG () const -> std::string override |
| A tag name when represented by XML. More... | |
| virtual auto | CHILD_TAG () const -> std::string override |
| A tag name of children. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::EntityGroup< _Container, _ETy, T > Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::EntityGroup< _Container, _ETy, T > | |
| EntityGroup () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| auto | has (const std::string &key) const -> bool |
| Indicates whether a container has an object having the specified identifier. More... | |
| auto | get (const std::string &key) -> value_type & |
| Access the element by specified identifier(key). More... | |
| auto | get (const std::string &key) const -> const value_type & |
| Access the const element by specified identifier(key). More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::Entity Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::Entity | |
| Entity () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IEntityGroup | |
| IEntityGroup () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IClient Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IClient | |
| IClient () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| virtual void | listen () |
| Listens message from a related system. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IProtocol Public Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IProtocol | |
| IProtocol () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual auto | createChild (std::shared_ptr< library::XML >) -> ExternalSystemRole *override |
| Factory method of a child Entity. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IClient Protected Member Functions inherited from samchon::protocol::IClient | |
| virtual auto | BUFFER_SIZE () const -> size_t |
| Buffer size of network I/O. More... | |
| virtual void | _replyData (std::shared_ptr< Invoke >) |
| A method for pre-processing replied Invoke message. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| size_t | inProgress |
| A number of processes running on the distributed system. More... | |
| size_t | processed |
| A number of processed have runned. More... | |
| double | avgElapsedTime |
| Average of elapsed time. More... | |
| double | performance |
| A performance index. More... | |
| DSRoleHistoryList * | roleHistoryList |
| A list of history log for role allocations. More... | |
| DSInvokeHistoryArray * | invokeHistoryArray |
| A list of history log for reported Invoke messages. More... | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem Protected Attributes inherited from samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem | |
| std::string | name |
| A name can identify an external system. More... | |
| std::string | ip |
| An ip address of an external system. More... | |
| int | port |
| A port number of an external system. More... | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from samchon::protocol::IClient Protected Attributes inherited from samchon::protocol::IClient | |
| Socket * | socket |
| Socket for network I/O. More... | |
| std::mutex * | sendMtx |
| A mutex for sending message. More... | |
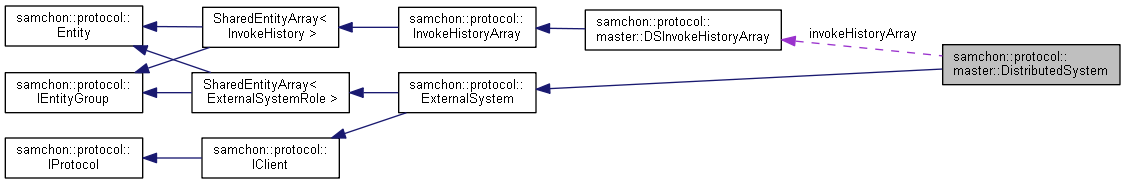
A network driver for a distributed system.
DistributedSystem class is an ExternalSystem having role as DistributedSystemRole objects with performance index and history log allocation of DistributedSystemRole objects and have requsted Invoke message to related external system.
The greatest difference between DistributedSystem and ExternalSystem is, unlike the ExternalSystem class which having is ExternalSystemRole objects exclusively, DistributedSystem does not monopoly a DistributedSystemRole. The DistributedSystemRole can allocatedto multiple DistributedSystem.
DistributedSystem and DistributedSystemRole classes have performance index and history log archiving what they've requested to the related distributed system. Allocating DistributedSystemRole objects to DistributedSyste will be determined those performance index and history log for optimize distribution of elasped time about each Invoke message processing.
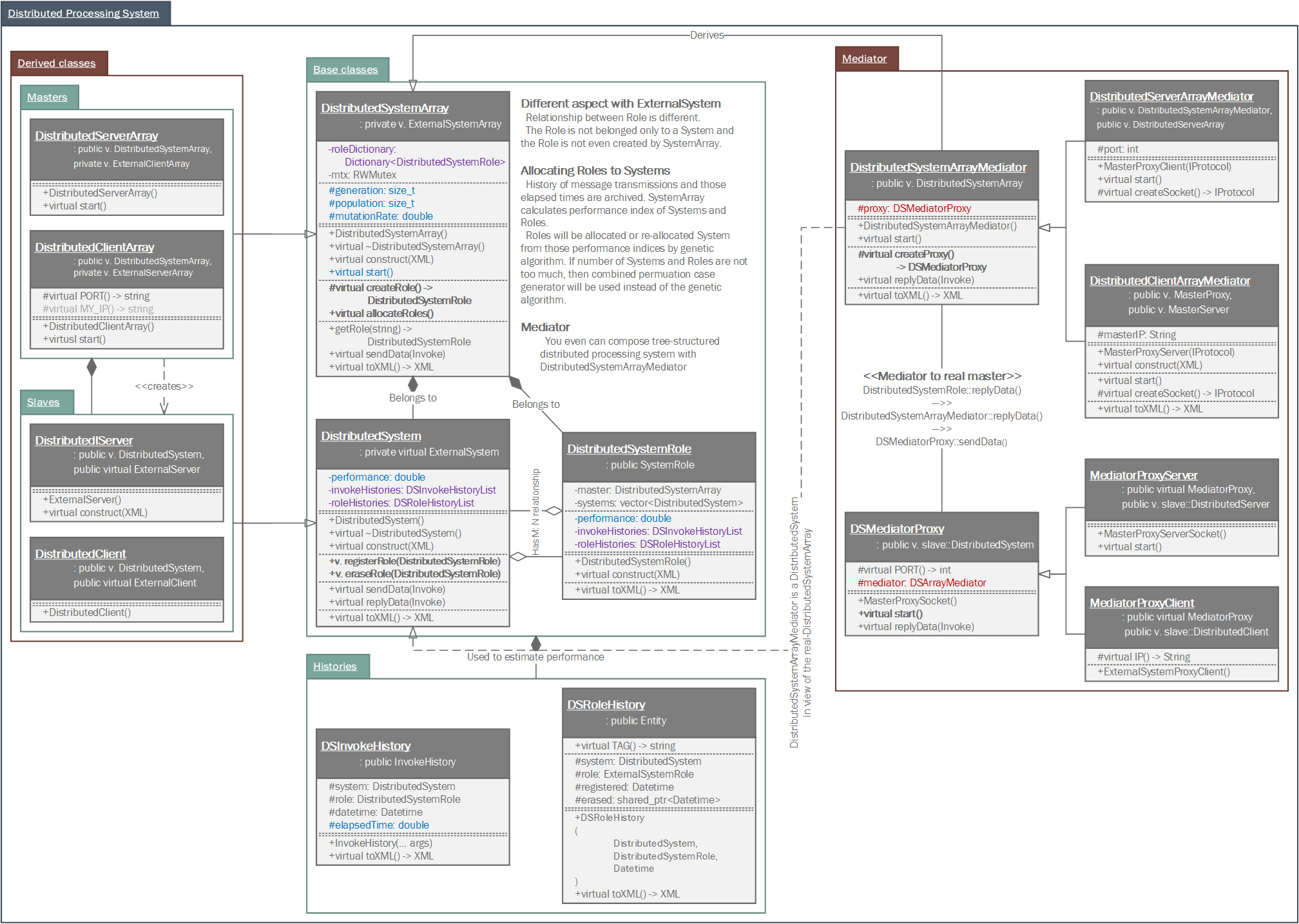
ExternalSystem is a boundary class interacting with an external system by network communication. Also, ExternalSystem is an abstract class that a network role, which one is server and which one is client, is not determined yet.
The ExternalSystem has ExternalSystemRole(s) groupped methods, handling Invoke message interacting with the external system, by subject or unit of a moudle. The ExternalSystemRole is categorized in a 'control'.
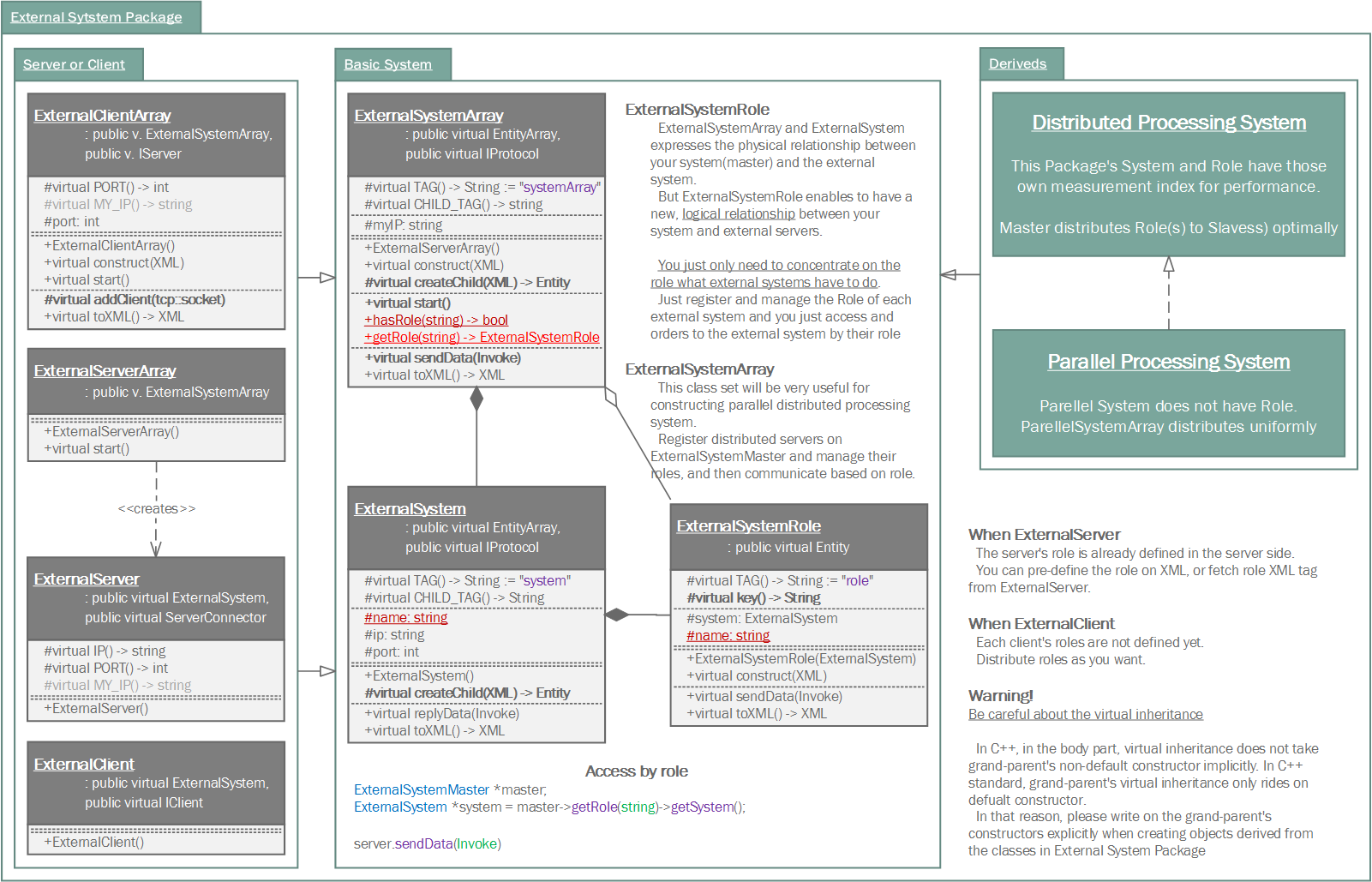
The ExternalSystem class takes a role of interaction with external system in network level. However, within a framework of Samchon Framework, a boundary class like the ExternalSystem is not such important. You can find some evidence in a relationship between ExternalSystemArray, ExternalSystem and ExternalSystemRole.
Of course, the ExternalSystemRole is belonged to an ExternalSystem. However, if you access an ExternalSystemRole from an ExternalSystemArray directly, not passing by a belonged ExternalSystem, and send an Invoke message even you're not knowing which ExternalSystem is related in, it's called "Proxy pattern".
Like the explanation of "Proxy pattern", you can utilize an ExternalSystemRole as a proxy of an ExternalSystem. With the pattern, you can only concentrate on ExternalSystemRole itself, what to do with Invoke message, irrespective of the ExternalSystemRole is belonged to which ExternalSystem.
Definition at line 44 of file DistributedSystem.hpp.
| DistributedSystem::DistributedSystem | ( | ) |
Default Constructor.
Definition at line 19 of file DistributedSystem.cpp.
References invokeHistoryArray.
|
overridevirtual |
Construct data of the Entity from an XML object.
Constructs the EntityGroup's own member variables only from the input XML object.
Do not consider about constructing children Entity objects' data in EntityGroup::construct(). Those children Entity objects' data will constructed by their own construct() method. Even insertion of XML objects representing children are done by abstract method of EntityGroup::toXML().
Constructs only data of EntityGroup's own.
Overrides the construct() method and fetch data of member variables from the XML.
By recommended guidance, data representing member variables are contained in properties of the put XML object.
| xml | An xml used to construct data of entity |
Reimplemented from samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem.
Reimplemented in samchon::protocol::master::DistributedServer.
Definition at line 29 of file DistributedSystem.cpp.
References samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem::construct(), and performance.
|
overrideprotectedvirtual |
Factory method of a child Entity.
EntityGroup::createChild() is a factory method creating a new child Entity which is belonged to the EntityGroup. This method is called by EntityGroup::construct(). The children construction methods Entity::construct() will be called by abstract method of the EntityGroup::construct().
Implements samchon::protocol::EntityGroup< _Container, _ETy, T >.
Definition at line 36 of file DistributedSystem.cpp.
|
overridevirtual |
Sends message to a related system.
| invoke | Invoke message to send |
Reimplemented from samchon::protocol::IClient.
Definition at line 49 of file DistributedSystem.cpp.
References invokeHistoryArray, and samchon::protocol::IClient::sendData().
|
overridevirtual |
Handling replied message from an external system.
If there's a related ExternalSystemRole, shifts responsibility to the ExternalSystemRole.
| invoke | Replied Invoke message |
Reimplemented from samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem.
Definition at line 67 of file DistributedSystem.cpp.
|
overridevirtual |
Get an XML object represents the EntityGroup.
Archives the EntityGroup's own member variables only to the returned XML object.
Do not consider about archiving children Entity objects' data in EntityGroup::toXML(). Those children Entity objects will converted to XML object by their own toXML() method. The insertion of XML objects representing children are done by abstract method of EntityGroup::toXML().
Archives only data of EntityGroup's own.
Returns an XML object that can represents the Entity containing member variables into properties.
A member variable (not object, but atomic value like number, string or date) is categorized as a property within the framework of entity side. Thus, when overriding a toXML() method and archiving member variables to an XML object to return, puts each variable to be a property belongs to only an XML object.
Don't archive the member variable of atomic value to XML::value causing enormouse creation of XML objects to number of member variables. An Entity must be represented by only an XML instance (tag).
| Standard Usage | Non-standard usage abusing value |
|---|---|
| <memberList> <member id='jhnam88' name='Jeongho+Nam' birthdate='1988-03-11' /> <member id='master' name='Administartor' birthdate='2011-07-28' /> </memberList> | <member> <id>jhnam88</id> <name>Jeongho+Nam</name> <birthdate>1988-03-11</birthdate> </member> |
Reimplemented from samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem.
Reimplemented in samchon::protocol::master::DistributedServer.
Definition at line 75 of file DistributedSystem.cpp.
References invokeHistoryArray, performance, samchon::protocol::ExternalSystem::toXML(), and samchon::protocol::EntityGroup< _Container, _ETy, T >::toXML().
|
protected |
A number of processes running on the distributed system.
Adds one count when sendData() is called and minus one count if a DSInvokeHistory, which means reported Invoke history, was reported by replyData().
If an DistributedSystemRole is allocated to multiple DistributedSystem objects, which DistributedSystem will be used is determined by the process size and performance index of the ExternalSystemRole.
Definition at line 67 of file DistributedSystem.hpp.
|
protected |
A number of processed have runned.
Definition at line 72 of file DistributedSystem.hpp.
|
protected |
Average of elapsed time.
Average elapsed time of handling Invoke message (request) in frame work of tbe related distributed system. Not in frame work of distributed system's driver, DistributeDSystem.
The ultimate optimization target of distributed processing system is to minimizing standard deviation of the average elapsed time of the DistributedSystem.
Definition at line 84 of file DistributedSystem.hpp.
|
protected |
A performance index.
A performance index z is calculated by normalization calculating reverse number of whole distributed system's average elapsed times and its z value between the normal distribution.
If a distributed system has no history of handling Invoke message, then set the performance index to 0 as default. The performance index will be re-calcuated whenever re-allocation of roles is done (DistributedSystem::allocateRoles()).
Definition at line 103 of file DistributedSystem.hpp.
Referenced by construct(), and toXML().
|
protected |
A list of history log for role allocations.
Definition at line 108 of file DistributedSystem.hpp.
|
protected |
A list of history log for reported Invoke messages.
Definition at line 113 of file DistributedSystem.hpp.
Referenced by DistributedSystem(), sendData(), and toXML().